What is MTHFR C677T?
Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase is labeled for both an enzyme and a gene. The MTHFR C677T gene produces a functioning MTHFR enzyme that converts methyfolate to 5-MTHF and helps regulate homocysteine levels. If the MTHFR C677T gene has heterozygous or homozygous variants, the enzyme is slowed down, and folate does not effectively convert to the active 5-MTHF (methylfolate).
My MTHFR Gene is Heterozygous or Homozygous: What Does that Mean?
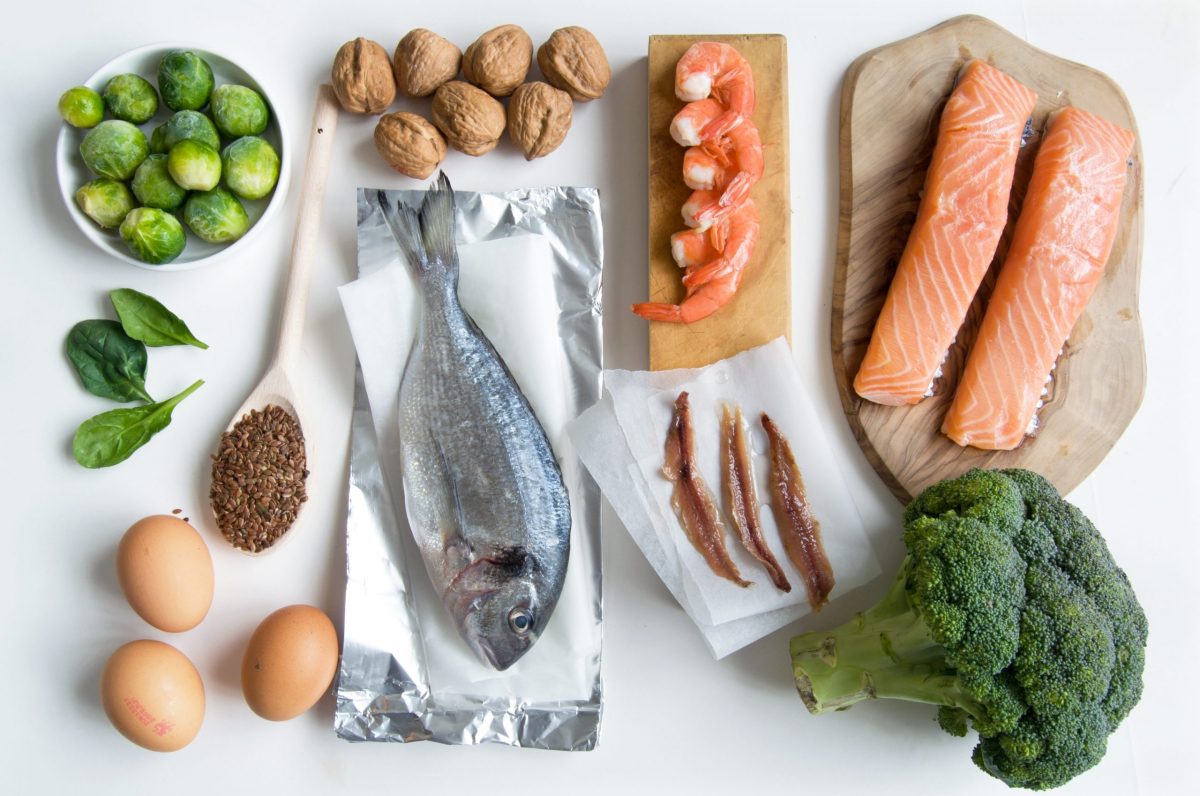
If you have a heterozygous or homozygous MTHFR C677T polymorphism, you may have an increased need for B2 and dietary methylfolate for healthy homocysteine levels, fertility, pregnancy, and BH4 levels.
Low levels of BH4 are linked to low levels of the neurotransmitters, including serotonin, dopamine, melatonin, norepinephrine and epinephrine. Therefore, MTHFR can affect mood disorders. BH4 also play a role in the detoxification of ammonia (by-product of protein metabolism). It is possible that high amounts of muscle meats may create too much ammonia in people with the homozygous MTHFR C677T gene, and this genotype is pointing more towards a plant-based diet rich in folate.
The FUT2 gene is also relevant when looking at MTHFR due to its relationship to bifidus levels. Probiotics – like bifidus – are vitamin producing factories, producing all of the B-vitamins. Healthy FUT2 function with a change in diet that increases bifidobacteria in the gut through prebiotic intake will increase folate levels.
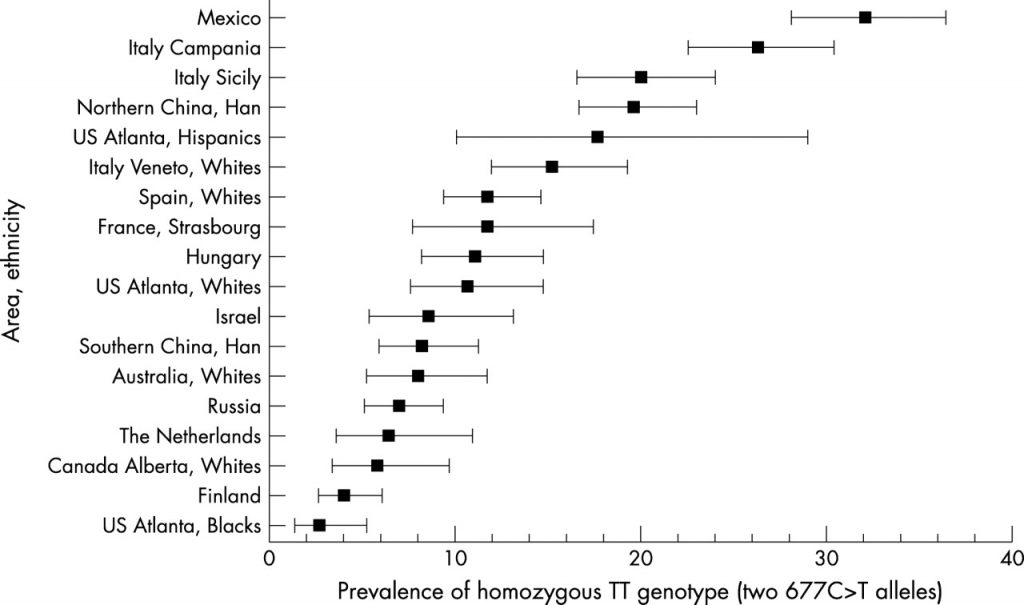
Where are the Highest Clusters of the Homozygous C677T MTHFR Genotype Found?
At Nutrition Genome, we find it extremely important to understand genotypes in the perspective of environmental adaptation. Many genes have both strengths and weaknesses, and understanding both sides of a gene can help remove any fear and the notion that not all genotypes are inherently better than another.
As you can see in the chart below, the highest rates of the homozygous genotype are in places with temperate to hot weather, where you also find the highest rates of folate-rich plants are growing.
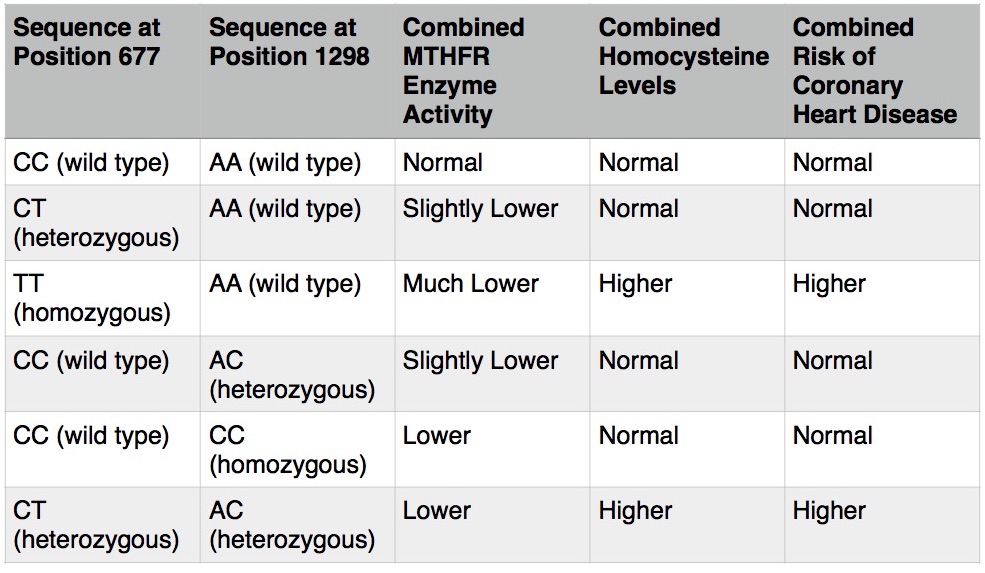
What is the Difference Between a Heterozygous and Homozygous MTHFR C677T?
As you will see in the table below, a heterozygous MTHFR does not always mean folate and B12 supplementation are needed. This is why it is important to look at all the other genes/enzymes in the methylation cycle to determine the exact nutrient needs for healthy homocysteine.
This study found that carriers of the T/T genotype required 800 mcg of dietary folate, while C/C required only 200 mcg of dietary folate to stay below the target homocysteine level. This study shows unequivocally that dietary folate has quantitatively different effects on genotype.
Supplementing with 5-MTHF is essentially bypassing this enzyme. High dosing of 5-MTHF(1mg or more) however can cause high nitric oxide levels leading to anxiety and panic attacks, especially those with low protein diets, low electrolytes, and SNPs in COMT, SOD, and glutathione.
Since niacin is the solution to this reaction, consuming foods with the full-spectrum of B-vitamins may be the best approach along with supporting the other genes and enzymes involved.
Methylfolate vs. Folinic Acid for MTHFR 677
Like methylfolate, folinic acid is a food-based folate that enters the folate cycle and is converted to methylfolate. In a 2023 study, the MTHFR 677 TT homozygous genotype had a higher reduction in lowering homocysteine with methylfolate, while the heterozygous CT genotype had a higher reduction in homocysteine with folinic acid.
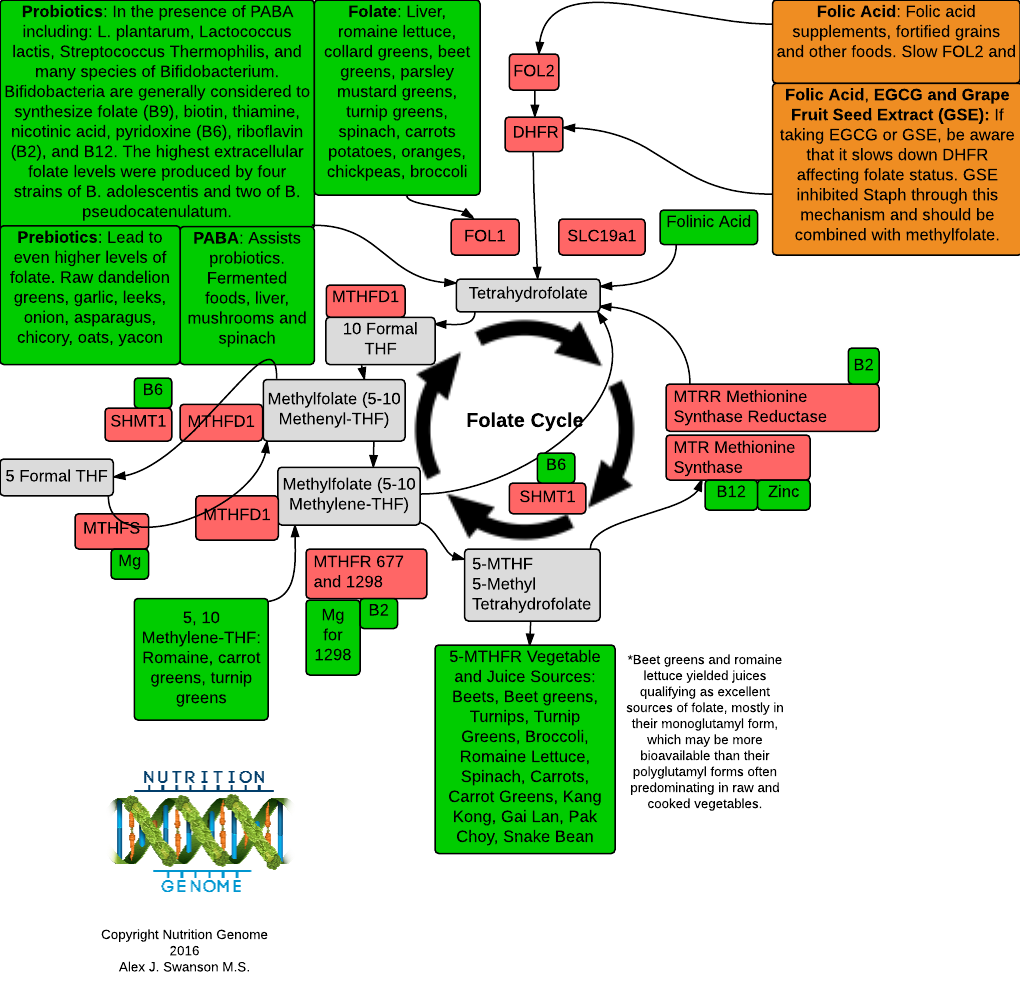
The Folate Methylation Cycle
When factoring all of the genes and nutrients involved in the folate methylation process, you can better determine folate needs.
The Nutrition Genome Report factors all of these in to the final analysis.