What is the APOE Gene?
APOE is a cholesterol transporter and functions as a key regulator to coordinate the mobilization of cholesterol between cells and remove toxins. These functions are particularly critical for the nervous system where the APOE transport of cholesterol is critical for the maintenance of brain neurons.
Two homozygous APOE genes determine the e4 genotype. The e4 genotype is found today in 15% of individuals and is the one most correlated to late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. The risk of cognitive decline conferred by carrying the E4 allele is greater among people from northern Europe.
The e4 allele was common in our hunter-gatherer ancestors and is still highly prevalent in remaining foraging societies. The e3 allele (found in 78% of people) is the most common in humans, especially in regions with a long-established agricultural economy showing the mutation likely occurred during our change to an agricultural diet.
Alzheimer’s Disease and APOE
The first thing you should know is that many individuals with the APOE-ε4 allele never develop Alzheimer’s and many patients with Alzheimer’s disease do not have the APOE-ε4 allele. Knowing if you are APOE-ε4 appears to be useful as part of the entire genetic blueprint in determining dietary and exercise needs to prevent Alzheimer’s if it runs in your family.
While over 60% of people with Alzheimer’s disease harbor at least one APOE-ε4 allele, it has been recommended that the APOE-ε4 test is not to be used for the prediction of Alzheimer’s disease risk because there are many other epigenetic factors at play.
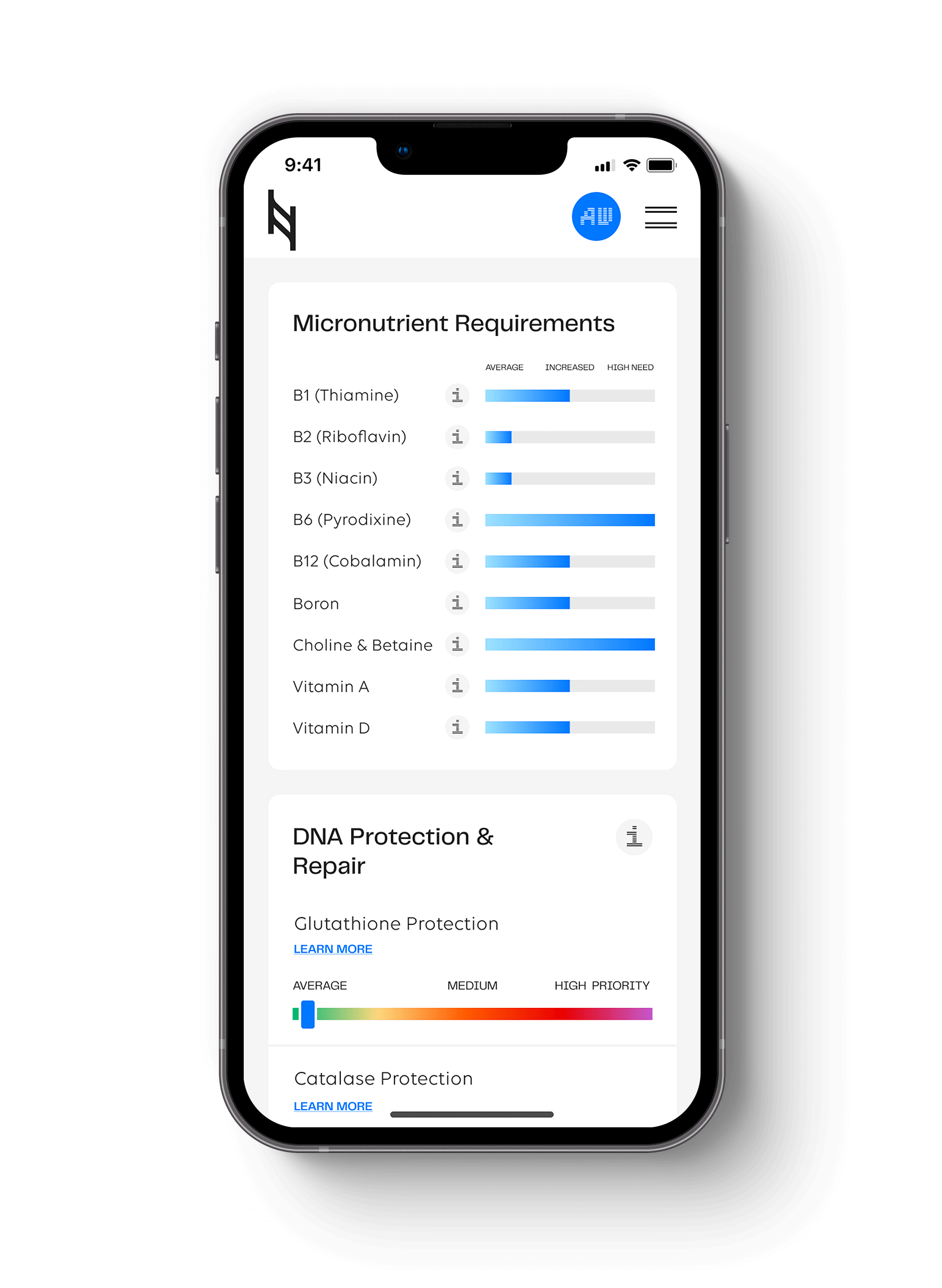
Postmenopausal women constitute more than 60% of the affected Alzheimer’s population, highlighting a potential estrogen connection. It is recommended that you look at ACSL1, TCF7L2, PEMT, CAT, SOD2, GPX, MTHFR, FUT2, and BDNF genes in the Nutrition Genome Report for a more comprehensive perspective on the pathways associated with Alzheimer’s disease and strategies to prevent it.
Understanding the Connection of Alzheimer’s Disease to APOE
Some of you read about the Tp53 gene in your Nutrition Genome Report. Variants in this gene increased the probability of conception in cold weather, showing an adaptation to the climate for procreation. The downside is that it increases the sensitivity to the UV rays of the sun for those of us who moved from a northern climate to a southern climate.
APOE-ε4 is a gene that confers an advantage in one period of life but later presents as a disadvantage. During the hunter-gatherer era, APOE-ε4 appeared beneficial in protecting against miscarriage, stillbirth, and diseases evoked by infectious diseases. The trade-off, however, was decreased injury repair to the brain later in life that most likely didn’t occur during the hunter-gatherer era due to a shorter life span.
So it made more sense for our species to select APOE-ε4 because early life survival was a bigger threat. APOE-ε4 carriers have also been shown to exhibit cognitive benefits earlier in life and higher intestinal absorption of dietary vitamin D and calcium, promoting stronger bones.
I have the APOE-ε4 Genotype. What Should I Do?
#1 Lower Oxidative Stress
Compared to APOE-ε2 and APOE-ε3, APOE-ε4 is less effective in protecting cells from oxidative toxicity, and therefore the genes in the Antioxidant and Inflammation section of the Nutrition Genome Report are key. If you live in a city with higher rates of air pollution and you are female, this is going to be even more relevant.
#2 Avoid High-Risk Activities for Traumatic Brain Injuries
Increasing evidence has shown that APOE-ε4 genotype is associated with poorer outcomes following traumatic brain injury (TBI), likely due to the reduced ability to repair synapses and protect neurons from injury. TBIs are associated with an increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Look at your genes in the neurotransmitter section of the Nutrition Genome Report, especially those connected to glutamate and acetylcholine.
#3 Increase your Exercise and fast for 12-16 hours between Dinner and Breakfast
Both of these strategies have proven to be critical for positive APOE-ε4 function. Remember, this is a hunter-gatherer genotype, compounding the negative effects of a sedentary lifestyle and grain-based diet. Alcohol is also best avoided for e4 carriers. Research has shown that 30 minutes a day, 5 days a week of aerobic exercise essentially negates the risk of APOE-ε4.
#4 Sleep 8-9 hours each night
Sleep is where repair and detoxification take place. Studies have found that disturbed sleep amplifies the adverse effects of APOE-ε4 and increases the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Be aware that sleep aids that are anticholinergic drugs also increase the risk of cognitive decline. Melatonin, magnesium, valerian and other natural methods are recommended.
#5 Consider Ashwagandha and Lithium
Amyloid plaques are the sticky buildup of proteins that accumulate outside nerve cells. The current theory is that the APOE-ε4 genotype shows a reduced clearance of beta-amyloid. Researchers have demonstrated that when ashwagandha was added to β-amyloid treated samples, the toxic effects were neutralized and ashwagandha root extract was neuroprotective against β-amyloid induced neuropathogenesis.
Researchers have also found that continued lithium treatment was associated with a reduction in the rate of dementia and can actually be neuroprotective or even enhance the growth of neurons.
Summary
The APOE gene is associated with Alzheimer’s disease, but it cannot predict you getting it. Case studies have shown tremendous progress with diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes for slowing and even reversing symptoms.
Like all of our genes, the epigenetic expression through our diet, exercise, and lifestyle ultimately determines the function. For APOE-ε4, this means a more conscious regime of targeting key pathways if Alzheimer’s disease runs in your family.
Having this information along with the rest of your Nutrition Genome Report allows you to take control and modify the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. This has been validated with cardiovascular risk genes, and I believe future research will prove the epigenetic lifestyle changes with the genes associated with Alzheimer’s disease as well.
Find more strategies for Alzheimer’s disease in the Nutrition Genome Report.
You can also listen to the founder – Alex Swanson – interviewed on Alzheimer’s disease and APOE here: APOE4 & How to Prevent Alzheimer’s Disease.
Other Sources
1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4960866/
2. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26969397
3. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4202787/
4. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2842076/
5. https://academic.oup.com/cercor/article/17/8/1934/319393/Better-Memory-and-Neural-Efficiency-in-Young#ref-76
6. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15709483
7. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3797707/
8. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3859706/
Hit your health goals faster
We'll help you remove the guesswork
Experience the most advanced nutrigenomic test available, covering 100 clinically relevant genes for a "whole body" analysis. Take control of your health today.
$359