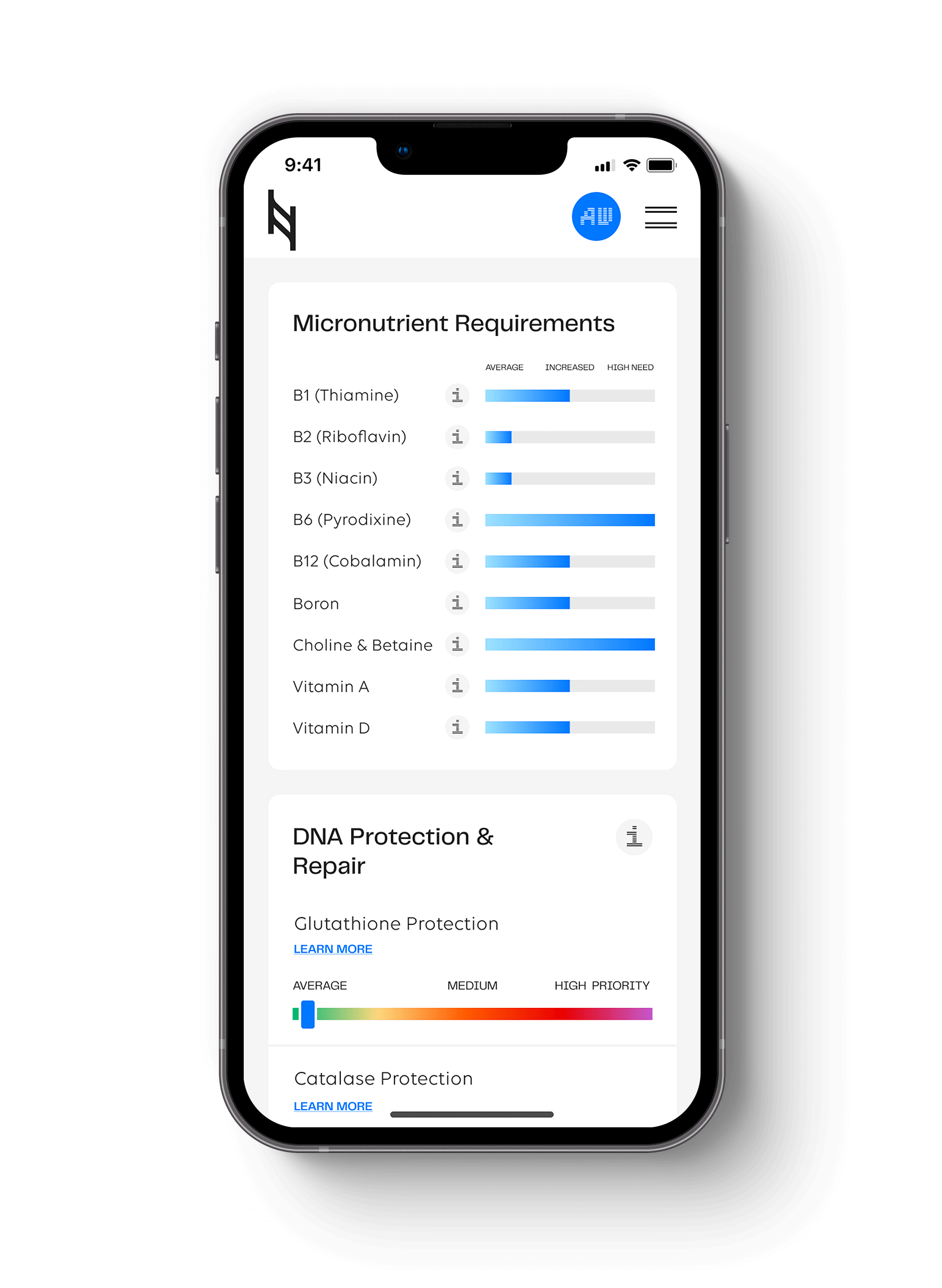
What is COMT?
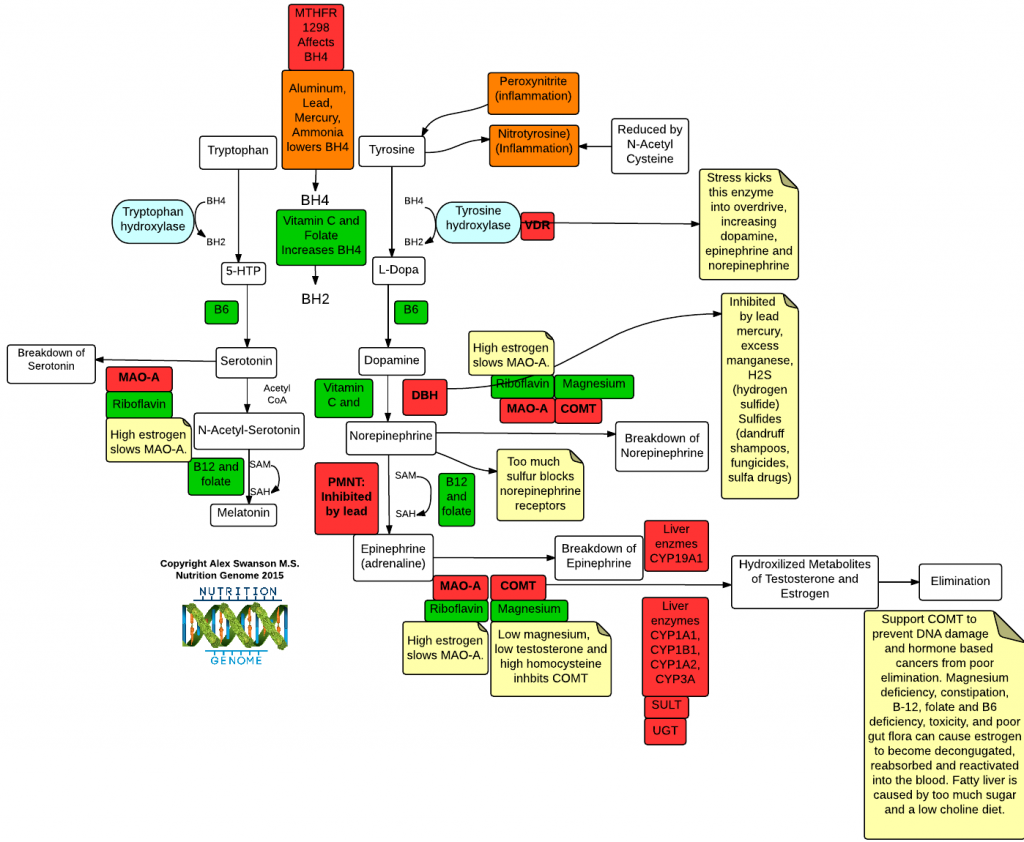
COMT (Catechol-O-Methyltransferase) breaks down estrogen, catecholamines and neurotransmitters including dopamine, epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Heterozygous or homozygous variants for the COMT V158M methionine allele slow down the COMT enzyme, affecting estrogen metabolism and the breakdown of dopamine and stress hormones. The valine variant catabolizes dopamine at up to four times the rate of the methionine variant while the methionine variant results in a 40% decrease in functional enzyme activity.
This alteration in enzymatic activity lead to anxiety, impulsiveness, obsessive behavior, ADHD, irritability (especially under stress), hyperactivity and abnormal behavior. From my own observation, I have found that those with higher dopamine levels do better in quiet environments, and are more affected by a lot of external noise and chaos. These are also the people who get easily anxious with coffee or can’t sleep if they have a glass of red wine too late.
However, the wild-type variants in COMT are also relevant. For these people, it is possible for COMT to be going too fast depending on hormonal status and other factors. In this case, it can be beneficial to increase catecholamine intake (berries, bananas, cacao, citrus, coffee, green tea, black tea, red wine) to slow down COMT and increase dopamine levels for an improved mood, concentration and focus.
The Warrior or Worrier Gene
COMT has been called the “warrior” or “worrier” gene based on the genotype. The wild-type COMT V158M genotype has been called the warrior genotype because there is a higher threshold of pressure to perform due to a lower baseline of dopamine. Stress slows down COMT, increasing dopamine and adrenaline levels. For the warrior genotype, certain types of pressure can actually be beneficial to perform at a higher level due to the dopamine boost.
The homozygous COMT V158M genotype has been referred to as the “worrier,” however, I would call this genotype the “problem solver.” The reason is that this genotype has naturally higher dopamine levels, which is an advantage for cognitive function in day to day life, especially complex problem solving. The downside is that this genotype can overreact to stress and pressure, creating dopamine and adrenaline levels that are too high, shutting the brain down.
You can read more about the Warrior or Worrier gene here, including where the heterozygous COMT V158M falls in this spectrum.
Factors that Could Further Slow or Speed Up COMT
Since COMT is working at a reduced rate for the heterozygous and homozygous variants, and it is potentially moving too fast for the wild-type variant, you want to avoid, minimize or increase certain lifestyle and diet factors based on the genotype.
- If you are homozygous AA for V158M, you may be more sensitive to catechols in green and black tea, wine, and coffee. It doesn’t mean these need to be avoided, but that you may obtain higher benefits with less and sensitive to more. For example, green tea has been found to be beneficial for breast cancer prevention in the AG and AA genotype because these individuals retained the polyphenols the longest. The wild type may need more to achieve the same benefit.
- For EGCG, there appear to be conflicting results for in vitro vs. in vivo. In vitro says that EGCG inhibits COMT. However, in vivo says it does not inhibit COMT and therefore should not pose any issue to COMT variants, even at higher doses.
- Magnesium supplementation may be necessary for COMT function while COMT activity is inhibited by high amounts of calcium/low magnesium supplementation and high iron.
- In vitro research has found that bisphenol (BPA) plastic bottles inhibit COMT activity. Plastic wrap, styrofoam cups, non-organic meat and dairy, non-organic plants sprayed with pesticides, unfiltered tap water, personal care and laundry products that contain parabens, artificial flavors and sweeteners and unfermented soy may also compound inhibition.
- Higher doses of supplemental vitamin C may be needed to modulate dopamine and adrenaline levels during stressful times.
- Beer is estrogenic due to hops, and IPA beers should be minimized by those with a homozygous COMT.
- Mercury toxicity also inhibits COMT activity through inhibition of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), a coenzyme for COMT.
- If S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) accumulates, the COMT enzyme may become impaired.
- High homocysteine levels slow down COMT further.
- With a COMT heterozygous or homozygous status, it has been clinically observed by physicians that people may have trouble with methyl donors. This can lead to ADHD, irritability, hyperactivity, or abnormal behavior. They may also be more sensitive to pain. Risk may be increased for some neuropsychiatric disorders and impaired estrogen metabolism.
- Testosterone speeds up the COMT and MAO-A pathway. Therefore, optimizing testosterone levels for men and women can be an excellent strategy for those exhibiting symptoms of high dopamine and adrenaline levels. See this article on the best exercises to target a slow COMT gene and high dopamine and adrenaline levels.
- The wild-type genotype may benefit from jobs with more pressure to perform, or activities that have an element of risk to boost dopamine, concentration and mood.
- The wild-type genotype may require more catecholamines to experience the same benefit as the AG or GG genotype receives at a lower dose.
How to Nutritionally Approach COMT?
The COMT enzyme requires the right dosage and type of magnesium based on weight and vitamin C which modulates dopamine and adrenaline. The other pathways to support include b-vitamins, and lowering excess estrogen levels for men or women through daily elimination. Interesting enough, magnesium and vitamin C is also the solution to constipation along with adequate fiber in the diet.
Catecholamine intake will vary depending on the spectrum of COMT function. If you have the AG or AA genotype for V158M, then catecholamine moderation is key. The GG genotype may benefit from more. Remember, diet and environmental factors epigenetically change COMT expression despite your genotype, so it is important to understand your current symptoms and if they are related to dopamine and adrenaline levels.
Hit your health goals faster
We'll help you remove the guesswork
Experience the most advanced nutrigenomic test available, covering 100 clinically relevant genes for a "whole body" analysis. Take control of your health today.
$359